
The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual is a comprehensive guide for healthcare providers, detailing procedures for specimen collection, handling, and testing. It ensures accurate and reliable results, covering key aspects like blood collection, fasting requirements, and specimen storage. This manual is essential for standardized practice and patient care.

Pre-Test Instructions for Patients
The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual provides essential guidelines for patients to prepare for their tests. Instructions include fasting requirements, avoiding certain medications, arriving early, and adhering to specific hygiene practices to ensure accurate test results.
Importance of Patient Preparation
Patient preparation is critical to ensuring accurate and reliable test results. Proper preparation helps minimize errors and avoids the need for repeat testing, which can delay diagnosis and treatment.
Fasting, avoiding certain medications, and adhering to hygiene practices are common requirements. These steps help standardize test conditions, reducing variability and ensuring consistency in results.
For example, fasting before a blood test prevents temporary changes in blood chemistry, which could lead to misleading conclusions. Similarly, avoiding specific medications ensures that test results reflect the patient’s natural condition rather than external influences.
Good preparation also enhances patient safety by reducing risks associated with incorrect test interpretations. Clinicians rely on accurate data to make informed decisions, making patient preparation a cornerstone of effective healthcare.
The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual provides detailed guidelines to help patients prepare correctly, ensuring the best possible outcomes for diagnostic testing.
Fasting Requirements
Fasting is often required before certain blood tests to ensure accurate results. The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual specifies that patients should abstain from food and beverages, except water, for a minimum of 8-12 hours before the test.
This period allows the body to clear digested food, preventing temporary changes in blood glucose, lipids, and other metabolic markers. Fasting is particularly crucial for tests like glucose tolerance, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels.
Patients should avoid alcohol and strenuous exercise during the fasting period, as these can influence test outcomes. However, medications prescribed by a doctor should be taken as usual, unless instructed otherwise.
It’s essential to follow these guidelines precisely, as failure to fast may result in misleading results, requiring retesting and delaying diagnosis. The manual provides clear instructions to help patients prepare correctly, ensuring reliable and actionable test results for their healthcare providers.
Blood Collection Procedures
Blood collection procedures outlined in the Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual ensure safe and efficient specimen acquisition. Venipuncture is the primary method, requiring proper technique to minimize discomfort and complications. The manual details steps for preparation, needle insertion, and post-collection care to maintain sample integrity and patient safety.
Venipuncture Techniques
Venipuncture is a critical skill in blood collection, requiring precision and care to ensure patient safety and sample integrity. The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual outlines best practices for venipuncture, emphasizing proper patient preparation, including positioning and tourniquet application. Phlebotomists are instructed to select appropriate needles and tubes based on the test requirements and patient factors, such as vein size and condition. The manual stresses the importance of maintaining a clean environment, using sterile equipment, and following aseptic techniques to prevent contamination. Patients should be informed and reassured to minimize anxiety, which can impact blood flow and collection success. Key steps include locating the vein, needle insertion at a 20-30 degree angle, and gentle aspiration of blood into collection tubes. Post-collection, pressure should be applied to the puncture site to prevent hematoma formation, and the patient should be monitored for any adverse reactions. Proper labeling and handling of specimens immediately follow to ensure accurate test results. These techniques are designed to optimize efficiency, safety, and consistency in blood collection processes.
Tube Selection and Labeling
Tube selection and labeling are vital steps in the blood collection process to ensure accurate test results and patient safety. The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual provides detailed guidelines for choosing the appropriate blood collection tubes based on the specific tests ordered. Different tubes are designed for various purposes, such as clot formation, plasma separation, or preserving glucose levels. Proper tube selection ensures that the correct additives or anticoagulants are used, preventing sample contamination or degradation. Labeling is equally critical, as it ensures that specimens are correctly identified and matched to the corresponding test requests. The manual emphasizes the importance of using pre-labeled tubes whenever possible and ensuring that all tubes are clearly marked with the patient’s name, date of collection, and test code. Labels must be legible, securely attached, and resistant to smudging or peeling. Adhering to these guidelines minimizes errors and ensures that specimens are processed correctly, maintaining the integrity of the testing process and delivering reliable results for accurate diagnosis. Proper tube selection and labeling are foundational to high-quality pathology services.
Specimen Handling and Storage

Proper handling and storage of specimens are crucial to maintain sample integrity. The Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual outlines guidelines for temperature control, avoiding contamination, and ensuring timely transportation to the laboratory for accurate test results.
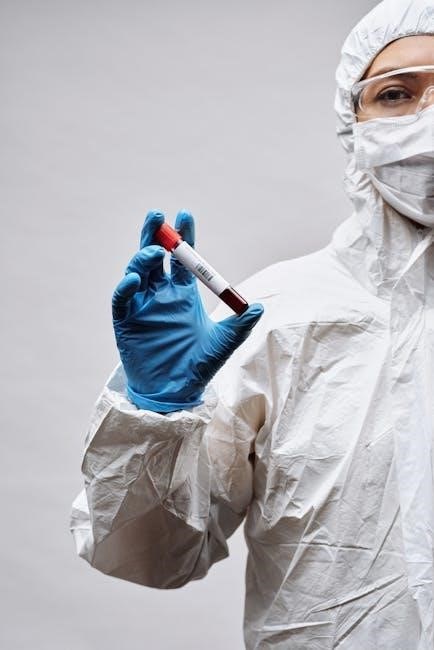

Proper Handling of Blood Tubes
Proper handling of blood tubes is essential to ensure accurate test results and maintain patient safety. According to the Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual, blood tubes should be mixed gently but thoroughly by inverting them 5-10 times immediately after collection. This step prevents clotting and ensures even distribution of additives. Tubes must be stored upright to avoid leakage and contamination. If multiple tubes are collected, they should be processed in the order of draw to prevent cross-contamination of additives.
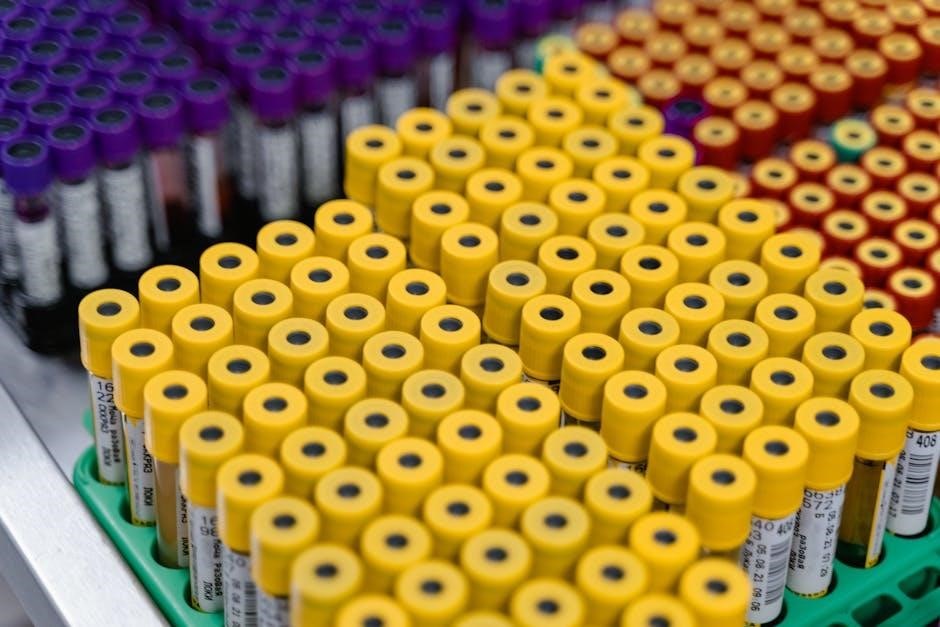

For certain tests, such as coagulation studies, tubes must be kept at room temperature and processed within specific timeframes. Tubes requiring refrigeration should be stored at 2-8°C but never frozen unless specified. Labels must remain legible, and tubes should be transported securely to the laboratory. Improper handling can lead to rejected samples or inaccurate results, emphasizing the importance of adhering to the manual’s guidelines.
Additionally, used needles and blood tubes should be disposed of in biohazard containers to minimize infection risks. By following these steps, healthcare professionals can ensure the integrity of blood samples and contribute to reliable diagnostic outcomes.
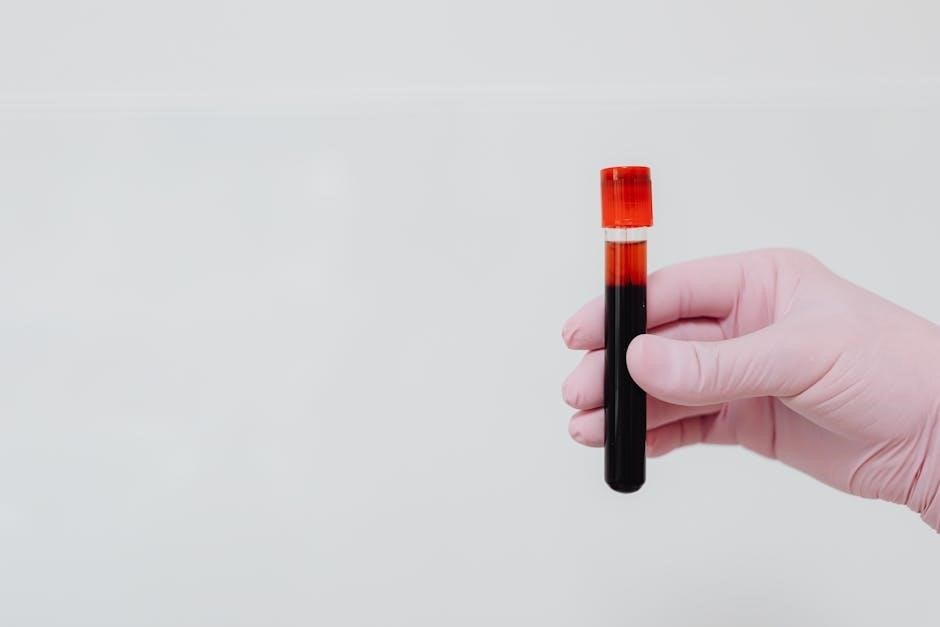

Labeling and Storage Guidelines
Accurate labeling and proper storage of specimens are critical for reliable test results. According to the Melbourne Pathology Test Collection Manual, all blood tubes and specimens must be labeled with the patient’s full name, date of birth, and the date and time of collection. This ensures traceability and prevents mix-ups. Labels should be clear, legible, and securely attached to avoid detachment during transport or processing.
Specimens must be stored in accordance with specific temperature requirements. Blood tubes for routine testing are typically stored at room temperature (20-25°C) unless otherwise specified. Certain tests, such as coagulation studies, may require refrigeration at 2-8°C. Freezing is generally avoided unless explicitly instructed for specific analyses.
During transport, specimens should be placed in sealed, leak-proof containers to prevent contamination. Tubes should remain upright to avoid spillage. Adherence to these guidelines ensures specimen integrity, accurate testing, and patient safety. Proper labeling and storage are essential for maintaining the quality of diagnostic specimens.
Always consult the manual for test-specific storage instructions to guarantee optimal results.